Verifier
This guide will walk you through setting up a simple React project using TypeScript and Vite, and integrate the TrustVC library to verify a W3C Verifiable Credential (VC) / OpenAttestation document. This tutorial focuses on non-transferable credentials.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following installed:
-
Node.js (version 18 or higher)
-
npm or yarn
-
A code editor, e.g., Visual Studio Code
Setting Up the React Project
1. Create a new project directory
mkdir verifier-project
cd verifier-project
2. Initialize the project
npm init -y
This creates a package.json file in your project directory.
3. Install required dependencies
npm install react react-dom vite-plugin-node-polyfills @trustvc/trustvc
npm install --save-dev typescript @vitejs/plugin-react @types/react @types/react-dom
4. Set up TypeScript configuration
Initialize TypeScript with the following command:
npx tsc --init
Update the tsconfig.json file as needed. For a basic setup, ensure the following options are included:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020",
"module": "ESNext",
"jsx": "react",
"strict": true,
"moduleResolution": "Node",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["src"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
5. Set up Vite (build tool):
Create a vite.config.ts file in the root directory and add the following content:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite';
import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react';
import { nodePolyfills } from 'vite-plugin-node-polyfills';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
react(),
nodePolyfills()
],
});
6. Add a basic project structure:
Create the following files and folders:
src/
├── App.tsx
├── main.tsx
└── index.css
Add the following content to App.tsx:
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { isValid, verifyDocument } from "@trustvc/trustvc";
const App: React.FC = () => {
const [verificationResult, setVerificationResult] = useState<{
VALIDITY: boolean;
DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY: boolean;
DOCUMENT_STATUS: boolean;
ISSUER_IDENTITY: boolean;
} | null>(null);
const [hasAttemptedUpload, setHasAttemptedUpload] = useState(false);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const handleFileDrop = async (event: React.DragEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
event.preventDefault();
setHasAttemptedUpload(true);
setIsLoading(true);
const file = event.dataTransfer.files[0];
if (!file) {
setIsLoading(false);
return;
}
try {
const fileContent = await file.text();
const vc = JSON.parse(fileContent);
// RPC provider url for interacting with the Amoy blockchain
const rpc = "https://rpc-amoy.polygon.technology";
const fragments = await verifyDocument(vc, rpc);
const result = isValid(fragments);
const documentIntegrity = isValid(fragments, ["DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY"]);
const documentStatus = isValid(fragments, ["DOCUMENT_STATUS"]);
const issuerIdentity = isValid(fragments, ["ISSUER_IDENTITY"]);
setVerificationResult({
VALIDITY: result,
DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY: documentIntegrity,
DOCUMENT_STATUS: documentStatus,
ISSUER_IDENTITY: issuerIdentity,
});
} catch (error) {
setVerificationResult(null);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
return (
<div
onDragOver={(e) => e.preventDefault()}
onDrop={handleFileDrop}
style={{ border: "2px dashed #ccc", padding: "20px", textAlign: "center" }}
>
<h1>Verify Documents</h1>
<p>Drop a Verifiable Credential file here to verify</p>
{isLoading && <div className="spinner">Verifying...</div>}
{hasAttemptedUpload && !isLoading && !verificationResult && (
<p style={{ color: "red" }}>File is not valid or could not be verified.</p>
)}
{!isLoading && verificationResult && (
<div>
<div>
<h2>VALIDITY</h2>
<ul>
<li>{verificationResult?.VALIDITY ? "true" : "false"}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<h2>DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY</h2>
<ul>
<li>{verificationResult?.DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY ? "true" : "false"}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<h2>DOCUMENT_STATUS</h2>
<ul>
<li>{verificationResult?.DOCUMENT_STATUS ? "true" : "false"}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<h2>ISSUER_IDENTITY</h2>
<ul>
<li>{verificationResult?.ISSUER_IDENTITY ? "true" : "false"}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
};
export default App;
Add the following content to main.tsx:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
import './index.css';
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
Create an index.html in the root directory:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Verifier</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script type="module" src="/src/main.tsx"></script>
</body>
</html>
7. Run the development server
Open your package.json file and add "dev": "vite" under the scripts section, like this:
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"dev": "vite"
}
Then run the following command to see the app running in the browser.
npm run dev
The verifier app is now ready.
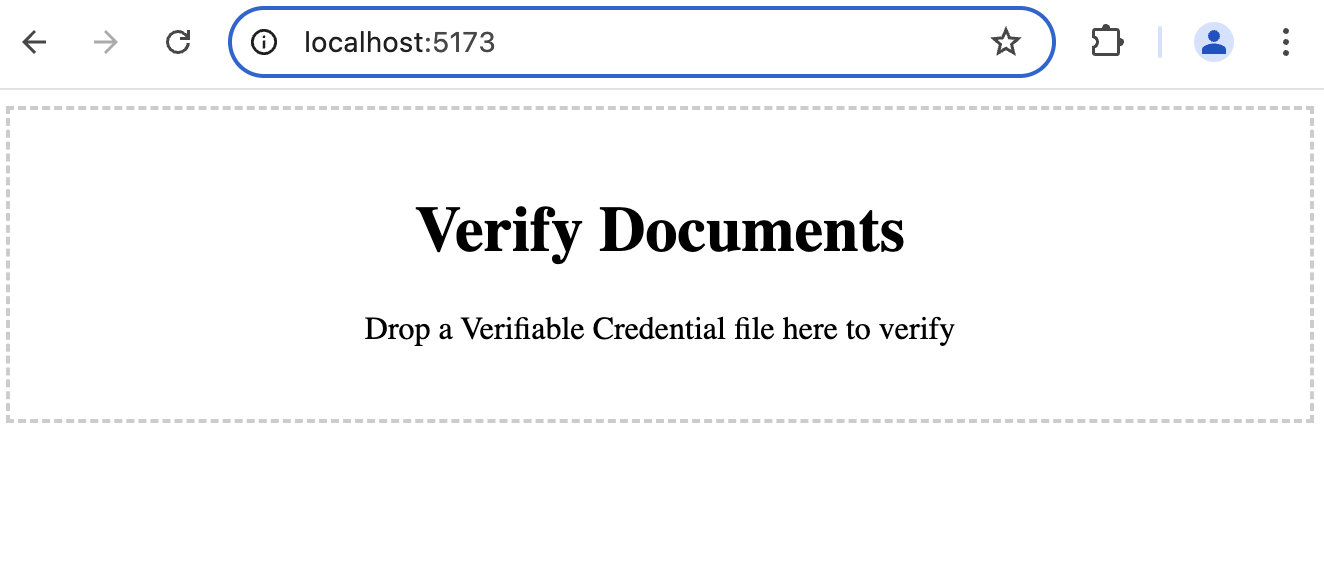
8. Source code and demo file
The source code for this project is also available on GitHub at TradeTrust/verifier-tutorial. You can explore the code, contribute, or make any modifications.
To test the verification process, you can use the demo file available at this link. You are free to modify this file or upload your own document to see how the verification process works.
Default verification
By default, the provided verifyDocument method performs various checks on a document depending on its type. These checks ensure the integrity, status, and identity of the document and its issuer. Below are the verifiers and their categories for OpenAttestation and W3C.
OpenAttestation Verifiers
The verifiers for OpenAttestation are categorized as follows:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| openAttestationHash | DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY | Verify that merkle root and target hash matches the certificate |
| openAttestationDidSignedDocumentStatus | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify the validity of the signature of a DID signed certificate |
| openAttestationEthereumDocumentStoreStatus | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify the certificate has been issued to the document store and not revoked |
| openAttestationEthereumTokenRegistryStatus | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify the certificate has been issued to the token registry and not revoked |
| openAttestationDidIdentityProof | ISSUER_IDENTITY | Verify identity of DID (similar to OpenAttestationDidSignedDocumentStatus) |
| openAttestationDnsDidIdentityProof | ISSUER_IDENTITY | Verify identity of DID certificate using DNS-TXT |
| openAttestationDnsTxtIdentityProof | ISSUER_IDENTITY | Verify identity of document store certificate using DNS-TXT |
The OpenAttestation verifiers are exported as openAttestationVerifiers.
W3C Verifiers
The verifiers for W3C are categorized as follows:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| w3cSignatureIntegrity | DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY | Verify the signature of a W3C Verifiable Credential |
| w3cCredentialStatus | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify the credential status of a W3C Verifiable Credential |
| w3cEmptyCredentialStatus | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify for cases where no credential status is defined |
| credentialStatusTransferableRecordVerifier | DOCUMENT_STATUS | Verify for W3C Verifiable Credential issued as transferable records |
| w3cIssuerIdentity | ISSUER_IDENTITY | Verify the identity of the issuer in the W3C Verifiable Credential |
The W3C verifiers are exported as w3cVerifiers.
Custom verification
You can build your own verify method or your own verifiers:
import { verificationBuilder, openAttestationVerifiers, w3cVerifiers } from "@trustvc/trustvc";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
// Provider configuration for interacting with the Amoy blockchain
const provider = new ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider("https://rpc-amoy.polygon.technology");
/**
* Verification function for OpenAttestation (OA) documents.
* Uses OpenAttestation verifiers to validate the integrity, authenticity, and status of OA documents.
* Equivalent to the default OA verifier provided by TrustVC.
*/
const verifyOA = verificationBuilder(openAttestationVerifiers, { provider });
/**
* Verification function for W3C Verifiable Credentials (VCs).
* Uses W3C verifiers to validate the integrity, authenticity, and compliance of W3C credentials.
* Equivalent to the default W3C verifier provided by TrustVC.
*/
const verifyW3C = verificationBuilder(w3cVerifiers, { provider });
Building a custom verification method
We will implement a verification method with the following rules:
- It should execute only for documents where the version is
https://schema.openattestation.com/2.0/schema.json. - It should return a valid fragment only if the document contains a
nameproperty with the valueCertificate of Completion
Rule 1: Verify document version
To enforce the version check, we will leverage the skip and test methods:
testMethod: Determines when the verification method should run.skipMethod: Explains why the verification was not executed.
We use the DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY type because the verification involves checking the document's content.
Rule 2: Validate the name property
After establishing when the verifier should execute, we define its core logic in the verify method. Using the getDataV2 utility, we can access the document's data and construct the appropriate fragment based on its content.
import { verificationBuilder, openAttestationVerifiers, Verifier, isValid, getDataV2 } from "@trustvc/trustvc";
import * as document from "./document.json";
const customVerifier: Verifier<any> = {
skip: async () => {
return {
status: "SKIPPED",
type: "DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY",
name: "CustomVerifier",
reason: {
code: 0,
codeString: "SKIPPED",
message: `Document doesn't have version equal to 'https://schema.openattestation.com/2.0/schema.json'`,
},
};
},
test: () => document.version === "https://schema.openattestation.com/2.0/schema.json",
verify: async (document: any) => {
const documentData = getDataV2(document);
if (documentData.name !== "Certificate of Completion") {
return {
type: "DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY",
name: "CustomVerifier",
data: documentData.name,
reason: {
code: 1,
codeString: "INVALID_NAME",
message: `Document name is ${documentData.name}`,
},
status: "INVALID",
};
}
return {
type: "DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY",
name: "CustomVerifier",
data: documentData.name,
status: "VALID",
};
},
};
Building a custom verify method
The verifyDocument function is built to run a list of verification method. Each verifier will produce a fragment that will help to determine if the document is valid. OpenAttestation comes with its own set of verification methods available in openAttestationVerifiers.
The verificationBuilder function helps you to create custom verification method. You can reuse the default one exported by the library.
Let's now build a new verifier using our custom verification method:
import { verificationBuilder, openAttestationVerifiers, Verifier, isValid, getDataV2 } from "@trustvc/trustvc";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
import document from "./document.json";
// Provider configuration for interacting with the Amoy blockchain
const provider = new ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider("https://rpc-amoy.polygon.technology");
const customVerifier: Verifier<any> = {
/* content has been defined in the section above */
};
// create your own verify function with all verifiers and your custom one
const verify = verificationBuilder([...openAttestationVerifiers, customVerifier], { provider });
const fragments = await verify(document);
console.log(isValid(fragments));
console.log(fragments.find((fragment: any) => fragment.name === "CustomVerifier")); // display the details on our specific verifier
Custom validation
Fragments would be produced after verifying a document. Each fragment will help to determine if the individual type mentioned here is valid or not, and would collectively prove the validity of the document.
The isValid function will execute over fragments and determine if the fragments produced a valid result. By default the function will return true if a document fulfill the following conditions:
- The document has NOT been tampered, AND
- The document has been issued, AND
- The document has NOT been revoked, AND
- The issuer identity is valid.
The function also allows a list of types to check for as a second parameter.
import { isValid, verifyDocument } from "@trustvc/trustvc";
import * as document from "./document.json";
// RPC provider url for interacting with any supported blockchain
const rpc = "any supported blockchain";
const fragments = await verifyDocument(document, rpc);
console.log(isValid(fragments, ["DOCUMENT_INTEGRITY"]));
console.log(isValid(fragments, ["DOCUMENT_STATUS"]));
console.log(isValid(fragments, ["ISSUER_IDENTITY"]));
console.log(isValid(fragments));