Overview
Building upon OpenAttestation framework, our Verifiable Document form one of two core pillars for TradeTrust framework.
In this tutorial guide, you will be deploying a verifiable document.
Goal
By the end of this guide, you would be able to create your 📜 Certificate of Completion that is valid on any compatible TradeTrust Verifier. The following guides are available:
- Issue a TradeTrust Verifiable document using DNS-DID method.
- (Advanced) Issue a TradeTrust Verifiable document that interacts with Ethereum Smart Contract.
Before we begin, lets take some time to understand the overall architecture of our verifiable documents.
Overview of Verifiable Documents (through a document store)
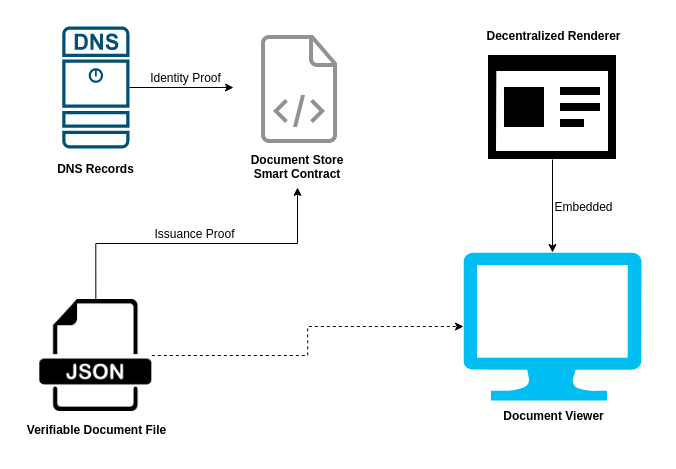
Document Store Smart Contract
The document store is a smart contract deployed onto the blockchain. When a TradeTrust document is issued, a proof of the issuance is stored onto the blockchain through the smart contract.
The smart contract is used to provide a globally consistent record for anyone to query a given TradeTrust document's issuance status.
DNS Records
A domain is required to issue a TradeTrust document. A DNS record must be inserted to the DNS to assert the identity of the TradeTrust document issuer.
Verifiable Document File
A Verifiable Document File is also known as the TradeTrust document. Machine-readable data of the TradeTrust document is stored in a .json file. In addition to the data, these .json files also contain information such as:
- claim of issuer's identity
- document rendering information
- document store smart contract
Decentralized Renderer
The decentralized renderer gives the TradeTrust document a human-readable look. It is essentially a website which will take a TradeTrust document data as input and display the document in a web view. This allows anyone to style their document without submitting code change to another party.
This tutorial will now require you to choose between the following options: